Four basic principles of deeply effective math teaching
If you were asked what were the most important principles in mathematics teaching, what would you say? I wasn't really asked, but I started thinking, and came up with these basic habits or principles that can keep your math teaching on the right track.
Principle 1: Let It Make Sense
Principle 2: Remember the Goals
Principle 3: Know Your Tools
Principle 4: Living and Loving Math
Principle 1: Let It Make Sense
Let us strive to teach for understanding of mathematical concepts and procedures, the "why" something works, and not only the "how".
This understanding, as I'm sure you realize, doesn't always come immediately. It may take even several years to grasp a concept. For example, place value is something kids understand partially at first, and then that deepens over a few years.

This is why many math curricula use SPIRALING: they come back to a concept the next year, and the next (and the next and the next...). Or, some curricula come back to a concept sooner than that... maybe every two weeks or so.
Now, spiraling can be very good if not done excessively. Unfortunately, some math curricula spiral concepts over so many years, and in such little pieces at a time, that they never teach the concepts and ideas in depth. Then some others have a "tight" spiral where each concept is revisited every few weeks, which then causes MOST of each lesson to be review problems — again causing a lack of focus and lack of depth.
Spiraling also presents this pitfall: it can cause parents/teachers to blindly "trust" the spiraling and think, "Well, he didn't get it this year... but he'll get it next year when the book comes back around to it." However, the presentation of that concept in the next year's schoolbook might be too difficult for such a child.
When it comes to spiraling, we need a BALANCE. Children do need review, but they also need a chance to focus on major concepts and get a fairly full picture of connecting thoughts (the depth).
The "how" something works is often called procedural understanding: the child knows HOW to work long division, or the procedure of fraction addition or fraction division, for example.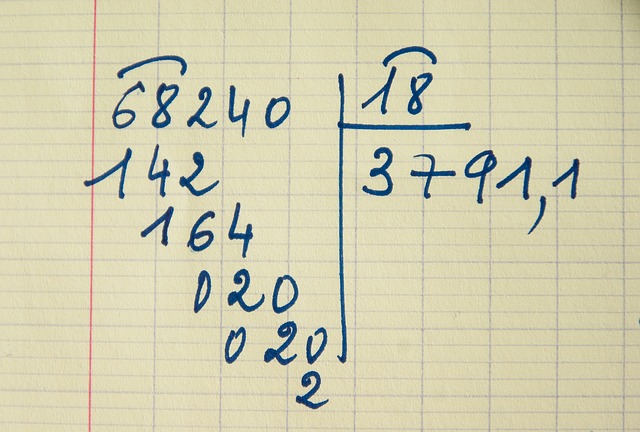 It is often possible to learn the "how" mechanically without understanding why it works. Procedures learned this way (via rote memory) are also often forgotten very easily!
It is often possible to learn the "how" mechanically without understanding why it works. Procedures learned this way (via rote memory) are also often forgotten very easily!
That is why in my Math Mammoth curriculum I have focused on the conceptual understanding so much. The child might learn the "HOW" quicker than he will learn the "WHY", but learning only the "HOW" will cause him to easily forget what has been learned. Plus, that will not help the child to learn to reason and make connections in mathematics.
The relationship between the "how" and the "why" — or between procedures and concepts — is complex. One doesn't always come totally before the other, and it also varies from child to child.
You can try alternating the instruction: teach how to add fractions, and let the student practice. Explain why it works. Go back to some practice. Back and forth. Sooner or later it should 'stick' — but it might be next year instead of this one, or after 6 months instead of in this month.
As a rule of thumb, don't totally leave a topic until the student both knows how, and understands the 'why'.
Tip: you can often test a student's understanding of a topic by asking him to PRODUCE an example, preferably with a picture or other illustration: "Tell me an example of multiplying fractions by whole numbers, and draw a picture." Whatever gets produced can tell the teacher a lot about what has been understood.
Principle 2: Remember the Goals
What are the goals of your math teaching? Are they...
- to finish the book by the end of school year...?
- make sure the kids pass the test...?
Or do you have goals such as:
- My student can add, simplify, and multiply fractions;
- My student can divide by 10, 100, and 1000.
These all are just "subgoals". But what is the ULTIMATE GOAL of learning school mathematics?
Consider these goals:
-
Students need to be able to navigate their lives in this ever-so-complex modern world. This involves dealing with taxes, loans, credit cards, purchases, budgeting, and shopping. Our youngsters need to be able to handle money wisely. All that requires good understanding of fractions, decimals, and percents.
Another very important goal of mathematics education as a whole is to enable the students to understand information around us. In today's world, this includes quite a bit of scientific information. Being able to read it and make sense of it requires understanding of big and small numbers, statistics, probability, and percents.
And then one more. We need to prepare our students for further studies in math and science. Not everyone ultimately needs algebra, but many do, and teens don't always know what profession they might choose or end up with.
I'd like to add one more broad goal of math education: teaching deductive reasoning. Naturally, high school geometry is a good example of this, but when taught properly, other areas of school math can do it as well.


The more you can keep these BIG REAL goals in mind, the better you can connect your subgoals to them. And the more you can keep the goals and the subgoals in mind, the better teacher you will be.
For example, adding, simplifying, and multiplying fractions all connects with a broader goal of understanding parts and whole. This will then lead to ratios, proportions, and percent. Another example: the mastery of all fraction operations is necessary for solving rational equations and manipulating rational expressions in algebra courses.
Tying in with the goals, remember that the BOOK or CURRICULUM is just a tool to achieve the goals — not a goal in itself. Don't ever be a slave of any math book!
Principle 3: Know Your Tools
A math teacher's tools are quite numerous nowadays.
First of all, of course, comes a black or white board, or paper — something to write on.

Then the basic measuring and geometric tools, such as a ruler, a compass, a protractor.
Then we also have software, animations, videos, and activities.
There are supplemental workbooks, math "readers", additional worksheets, and such.
And don't mention all the manipulatives, such as an abacus, scales, algebra tiles, fraction tiles, and so on.
And then there are games, games, games!
The choices are so numerous it's daunting. What's a teacher to do?
Well, you just have to get started somewhere, probably with the basics, and then add to your "toolbox" little by little as you have opportunity.
There is no need to try to use tons of tools all at once. It's important to learn how to use any tool you might acquire. Quantity won't equal quality. Knowing a few "math tools" inside out is more beneficial than a mindless dashing to find the newest activity or manipulative to spice up your math lessons.
Basic tools
- The board and/or paper to write on. Essential. Easy to use.
- The book or curriculum. Choosing a math curriculum is often difficult for homeschoolers. But keep in mind that no matter what curriculum you're using, YOU as the teacher have the control. Don't be a slave to the curriculum. You can skip pages, rearrange the order in which to teach the material, supplement it, and so on.
-
Concerning manipulatives: I once saw a question asked by a homeschooling parent, on the lines, "What manipulatives must I use and when?" The person was under the impression that manipulatives are a "must".
Manipulatives are definitely emphasized in these days. They are often useful, but they're not the end goal of math education, and there is no need to "go hog wild" over them. The idea is to help students learn to do the math without them!
Some manipulatives that I have found very helpful in the early grades are:
- Playing cards — when my youngest was about 3, he spent hours just organizing the cards in number order and also by color. Of course later on you can play games with them.
- Something to illustrate place value, especially with tens and ones (for Kindergarten). I made my daughter ten-bags by putting marbles into little plastic bags.
- A 100-bead abacus (for K-2)
- Some kind of fraction manipulatives. You can even simply make circular fraction models out of cardboard.
Often, drawing pictures can take the place of manipulatives, especially from middle elementary and on up.
- Measuring tools: rulers, scales, and measuring cups. These are essential in the early elementary grades in order to teach children about measuring units. They need that hands-on experience!
- Geometric tools: a ruler, a protractor, and a compass. Again, I feel these are very necessary.
- Math games: I believe in math games — they are often very enjoyable for children and thus quite motivating. I especially recommend games for drilling basic facts. For example, here's a card game that's worth 1000 worksheets.
And here's an ebook for you with LOTS of math card games: Acing Math.
Math Mammoth Light Blue series and Blue series products include lists of online games and activities for each math topic. These games and activities are also found in the lesson plans, where they are handily matched for each lesson in the Math Mammoth curriculum. - Math software: I definitely recommend the usage of some math software in algebra and calculus. I won't delve into the possibilities here; suffice it to say, Desmos is a popular and free online graphing calculator.
Principle 4: Living and Loving Math
You are the teacher. You show the way — also with your attitudes, your way of life.

Do you use math often in your daily life? Is using mathematical reasoning, numbers, measurements, etc. a natural thing to you every day?
And then: do you like math? Love it? Are you happy to teach it? Enthusiastic?
Both of these tend to show up in how you teach, but especially so in a homeschooling enviroment, because at home you're teaching your kids a way of life, and whether math is a natural part of it or not.
Math should not be a drudgery, nor something just confined to math lessons! It is said to be the "science of patterns". Just think how MUCH that definition actually includes!
Some ideas:

- Let it make sense. This alone can usually make quite a difference in making children to stay interested.
- When you use math in your daily life, explain how you're doing it, and include the children if possible. Figure it out together.
- Use fun math books, such as
- math puzzle books or
- Penrose the Mathematical Cat books (fun!)
- Try including a bit about math history. If you're interested in math history, check out Living Math for lesson plans for a family math history course.
By Maria Miller
Receive my monthly collection of math tips & resources directly in your inbox — and get a FREE Math Mammoth book!
You can unsubscribe at any time.
Math Mammoth TourConfused about the different options? Take a virtual email tour around Math Mammoth! You'll receive: An initial email to download your GIFT of over 400 free worksheets and sample pages from my books. Six other "TOURSTOP" emails that explain the important things and commonly asked questions concerning Math Mammoth curriculum. (Find out the differences between all these different-colored series!)This way, you'll have time to digest the information over one or two weeks, plus an opportunity to ask me personally about the curriculum. A monthly collection of math teaching tips & Math Mammoth updates (unsubscribe any time) We respect your email privacy.
Note: You will FIRST get an email that asks you to confirm your email address. If you cannot find this confirmation email, please check your SPAM/JUNK folder. |
"Mini" Math Teaching CourseThis is a little "virtual" 2-week course, where you will receive emails on important topics on teaching math, including:
- How to help a student who is behind You will also receive: A GIFT of over 400 free worksheets and sample pages from my books right in the very beginning.We respect your email privacy.
Note: You will FIRST get an email that asks you to confirm your email address. If you cannot find this confirmation email, please check your SPAM/JUNK folder. |
Maria's Math TipsEnter your email to receive math teaching tips, resources, Math Mammoth news & sales, humor, and more! I tend to send out these tips about once monthly, near the beginning of the month, but occasionally you may hear from me twice per month (and sometimes less often). Peek at the previous tips here. You will also receive:
We respect your email privacy.
|
|